 Read the Review Skills section. If there is any skill mentioned that you have not yet mastered,
review the material on that topic before reading the present chapter.
Read the Review Skills section. If there is any skill mentioned that you have not yet mastered,
review the material on that topic before reading the present chapter.
 Read the chapter quickly before the lecture that describes it.
Read the chapter quickly before the lecture that describes it.
 Attend class meetings, take notes, and participate in class discussions.
Attend class meetings, take notes, and participate in class discussions.
 Work the Chapter Exercises, perhaps using the Chapter Examples as guides.
Work the Chapter Exercises, perhaps using the Chapter Examples as guides.
 Study the Chapter Glossary.
Study the Chapter Glossary.
 Study all of the Chapter 3 Objectives. You might want to write a
description of how you will meet each objective. (Although it is best to master
all of the objectives, the following objectives are especially important because
they pertain to skills that you will need while studying other chapters of this
text: 3, 4, 8, 9, 13‑16, 21-28, 30, 31, 34, 35, and 37.)
Study all of the Chapter 3 Objectives. You might want to write a
description of how you will meet each objective. (Although it is best to master
all of the objectives, the following objectives are especially important because
they pertain to skills that you will need while studying other chapters of this
text: 3, 4, 8, 9, 13‑16, 21-28, 30, 31, 34, 35, and 37.)
 Reread Sample Study Sheet 3.1: Classification of Matter and
decide whether you will use it or some variation on it to complete the task it describes.
Reread Sample Study Sheet 3.1: Classification of Matter and
decide whether you will use it or some variation on it to complete the task it describes.
 Memorize the following. Be sure to check with your instructor to determine how much you
are expected to know of the following.
Memorize the following. Be sure to check with your instructor to determine how much you
are expected to know of the following.
The usual numbers of covalent bonds and lone pairs for the nonmetallic elements.
C - 4 bonds and no lone pairs
N, P - 3 bonds and 1 lone pair
O, S, Se - 2 bonds and 2 lone pairs
F, Cl, Br, I - 1 bond and 3 lone pairs
H - 1 bond and no lone pairs
Names and formulas of some binary covalent compounds.
water, H2O
ammonia, NH3
methane, CH4
ethane, C2H6
propane, C3H8
Prefixes
1, mon(o)-
2, di-
3, tri-
4, tetr(a)-
6, hex(a)-
5, pent(a)-
7, hept(a)-
8, oct(a)-
9, non(a)-
10, dec(a)-
|
Roots of nonmetallic elements
C, carb-
N, nitr-
O, ox-
F, fluor-
P, phosph-
S, sulf-,
Cl, chlor-
As, arsen-
Se, selen-
Br, brom-
I, iod-
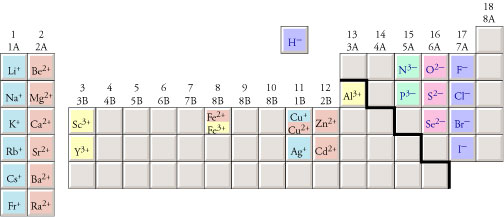
Charges on monatomic ions
Names and formulas for polyatomic ions
NH4+, ammonium
PO43-, phosphate
SO42-, sulfate
OH-, hydroxide
NO3-, nitrate
C2H3O2-, acetate
CO32-, carbonate
 Learn how to use a periodic table to classify the elements with respect to the following categories:
Learn how to use a periodic table to classify the elements with respect to the following categories:
Groups 1 to 18
Groups 1A to 8A
Alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, and noble gases
Metals, nonmetals, and metalloids
Representative (main‑group) elements, transition metals, and inner
transition metals
Periods 1 to 7
Solids, liquids, or gases at room temperature
 To get a review of the most important topics in the chapter, fill in the blanks in the Key Ideas section.
To get a review of the most important topics in the chapter, fill in the blanks in the Key Ideas section.
 Work all of the selected problems at the end of the chapter, and check your
answers with the solutions provided in this chapter of the study guide.
Work all of the selected problems at the end of the chapter, and check your
answers with the solutions provided in this chapter of the study guide.
 Ask for help if you need it.
Ask for help if you need it.
|
